First Aid Step 3 is a critical phase in emergency response‚ focusing on calling for professional help and providing advanced care․ This step ensures victims receive timely medical attention beyond basic first aid‚ emphasizing the importance of clear communication and quick decision-making to prevent further harm․
The Check‚ Call‚ Care method is central to this step‚ guiding individuals to assess situations‚ contact emergency services‚ and administer appropriate care․ It underscores the need for preparedness and knowledge to handle severe injuries or conditions effectively․
1․1 Overview of the Third Step in First Aid
The third step in first aid involves assessing the situation‚ calling for professional help‚ and providing care based on the victim’s condition․ This step is crucial for ensuring the victim receives appropriate medical attention beyond basic first aid․ It emphasizes the importance of clear communication with emergency responders and the use of available resources to stabilize the victim until professional help arrives․
Key actions include following the Check‚ Call‚ Care method‚ performing a secondary survey for injuries‚ and administering care such as controlling bleeding or managing burns․ Proper execution of this step can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further harm․ Timeliness and accuracy are critical․
1․2 Importance of Following the Third Step
Following the third step in first aid is critical to preventing the victim’s condition from worsening and ensuring proper medical intervention․ This step bridges the gap between initial care and professional help‚ making it essential for saving lives and reducing long-term damage․ Without adhering to this phase‚ victims may suffer from untreated injuries or delayed treatment‚ leading to more severe outcomes․ Proper execution of the third step ensures that first aid providers take responsibility for stabilizing the victim and facilitating a smooth transition to professional care․
It emphasizes accountability and preparedness‚ which are vital in emergency situations․

The Check‚ Call‚ Care Method
The Check‚ Call‚ Care method is a systematic approach to first aid‚ ensuring safety‚ prompt action‚ and effective care delivery in emergency situations․
2․1 Understanding the Three Cs in Emergency Response
The three Cs in emergency response—Check‚ Call‚ Care—provide a structured approach to managing emergencies effectively․ “Check” involves assessing the scene for safety and evaluating the victim’s condition‚ including their airway‚ breathing‚ and circulation (ABCs)․ “Call” requires contacting emergency services promptly to ensure professional help is on the way․ “Care” entails providing appropriate first aid‚ such as controlling bleeding or performing CPR‚ to stabilize the victim until help arrives․ This methodical process helps responders stay calm‚ prioritize actions‚ and deliver critical care efficiently‚ emphasizing safety‚ timely intervention‚ and effective assistance․
2․2 Practical Application of Check‚ Call‚ Care
The practical application of Check‚ Call‚ Care ensures a systematic response to emergencies․ Begin by checking the scene for hazards and assessing the victim’s condition‚ focusing on airway‚ breathing‚ and circulation (ABCs)․ Next‚ call emergency services‚ providing clear details about the situation and location․ Finally‚ care involves delivering appropriate first aid‚ such as CPR‚ controlling bleeding‚ or splinting injuries‚ while staying with the victim until professional help arrives․ This method ensures timely‚ effective‚ and safe assistance‚ prioritizing the victim’s well-being and preparing them for further medical intervention․ Regular training enhances the ability to apply these steps confidently and correctly․

Assessing the Situation and Calling for Help
Assess the area for safety and the victim’s condition․ Call emergency services promptly if serious injury or illness is present․ Be clear and precise․
3․1 When to Call Emergency Services
Call emergency services immediately if the situation is life-threatening or beyond basic first aid․ This includes severe injuries‚ difficulty breathing‚ chest pain‚ loss of consciousness‚ severe burns‚ or head injuries․ If the victim shows signs of shock‚ such as pale skin or rapid heartbeat‚ seek professional help․ For acute conditions like strokes or seizures‚ prompt medical intervention is critical․ Always err on the side of caution—calling earlier ensures faster response and better outcomes․ Delaying can worsen the condition‚ so recognize these red flags and act swiftly to alert emergency responders․
3․2 How to Effectively Communicate with Emergency Responders
To communicate effectively with emergency responders‚ stay calm and provide clear‚ concise information․ Begin by stating the nature of the emergency and the location․ Use specific details‚ such as street names or landmarks‚ to ensure responders can find the scene quickly․ Share key information‚ like the number of victims and visible injuries or symptoms․ Avoid unnecessary details and listen carefully to any instructions they provide․ Speak slowly and clearly‚ avoiding panic․ This ensures a swift and accurate response․ Proper communication is critical to saving time and lives in emergency situations․
3․3 The Role of Bystanders in Alerting Professionals
Bystanders play a crucial role in alerting professionals during emergencies․ Their immediate action can save precious time by calling emergency services or informing nearby authorities․ Bystanders should remain calm‚ assess the situation‚ and provide clear‚ accurate information to responders․ They can also assist by guiding emergency teams to the location or helping to secure the area․ However‚ bystanders should avoid interfering with professional care unless trained․ Their primary responsibility is to alert and provide essential details‚ ensuring a swift and effective response․ Timely intervention by bystanders can significantly improve outcomes in critical situations․
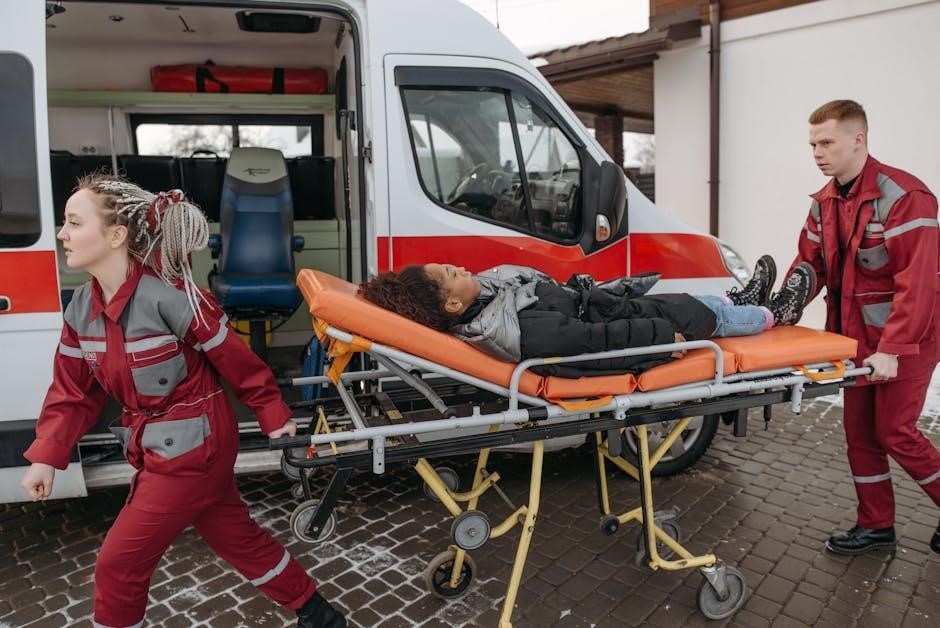
Providing Care After Initial Assessment
After assessing‚ provide care by controlling bleeding‚ immobilizing injuries‚ and managing breathing․ Use first aid kits to stabilize the victim until professional help arrives․
4․1 Administering Immediate Care Based on the Situation
Administering immediate care requires prompt action tailored to the injury or condition․ For bleeding‚ apply direct pressure with a clean cloth or bandage․ For burns‚ cool the area with cool water and cover it․ If the victim is unconscious‚ check their airway‚ breathing‚ and circulation (ABCs)․ Provide rescue breathing or CPR if necessary․ For fractures‚ immobilize the affected limb using splints or a sling․ In cases of shock‚ elevate the legs and keep the victim warm․ Always use resources like first aid kits wisely and avoid moving the victim unnecessarily unless danger persists․ Monitoring and reassessing the victim’s condition is crucial until professional help arrives․
4․2 Using First Aid Kits and Available Resources
A well-stocked first aid kit is essential for providing effective care․ It should include items like bandages‚ antiseptic wipes‚ gloves‚ and a first aid manual․ Always use resources appropriately based on the situation․ For example‚ apply bandages to control bleeding or use gloves to prevent direct contact with bodily fluids․ Improvise with available materials if necessary‚ such as using clean clothing to apply pressure․ However‚ rely on proper first aid supplies whenever possible․ Ensure the kit is easily accessible and restocked after use․ Familiarize yourself with the contents to act efficiently during emergencies‚ and check expiration dates of items regularly․
4․3 Monitoring the Victim Until Professional Help Arrives
Continuous monitoring of the victim is crucial until professional help arrives․ Always check for breathing‚ consciousness‚ and pulse․ Be alert to any changes in their condition‚ such as difficulty breathing‚ chest pain‚ or loss of consciousness․ Keep the victim calm and comfortable‚ and reposition them if necessary to improve breathing․ If trained‚ be prepared to start CPR if the victim’s condition worsens‚ such as if they stop breathing or their pulse is absent․ Ensure the victim stays warm to prevent shock and avoid moving them unnecessarily unless it’s unsafe to stay in the current location․ Stay with the victim until help arrives․
Documentation and Communication
Documenting incidents and maintaining clear communication are vital․ Record details like the injury‚ care provided‚ and the victim’s condition․ Ensure accurate information is shared with responders for effective assistance․
5․1 The Importance of Documenting the Incident
Documenting an incident is crucial for legal‚ medical‚ and procedural reasons․ It provides a clear record of what happened‚ the care provided‚ and the victim’s condition over time․ Accuracy is key‚ as this information helps emergency responders understand the situation upon arrival․ Documentation also serves as a reference for future medical needs and protects both the victim and the first aider legally․ It ensures continuity of care and accountability‚ making it an essential step in first aid protocols․ Always note details like injuries‚ treatments‚ and changes in condition to maintain a comprehensive and reliable record․
5․2 Communicating Clearly with Emergency Responders
Clear communication with emergency responders is vital to ensure effective assistance․ When calling for help‚ stay calm and provide concise information about the situation‚ including the location‚ number of victims‚ and severity of injuries․ Be specific about the care already provided‚ such as CPR or wound dressing‚ to avoid duplication of efforts․ Listen carefully to their instructions and follow any guidance they provide․ Avoid using jargon or unnecessary details‚ and ensure the line remains open if further updates are needed․ Clear‚ accurate communication helps responders prepare appropriately and act swiftly‚ improving outcomes for the victim․
5․3 Reporting the Incident to Relevant Authorities
Reporting the incident to relevant authorities is a crucial step in first aid․ It ensures that the incident is documented for legal and insurance purposes․ Accurate and timely reporting helps authorities take appropriate actions․ Include details like the nature of the incident‚ injuries sustained‚ and any first aid provided․ Different incidents may require reporting to different authorities‚ such as workplace safety officers or law enforcement․ Knowing who to report to and adhering to specific protocols is essential․ This step ensures accountability and proper follow-up‚ contributing to a safer environment and preventing future incidents․

Training and Resources for First Aid Step 3
Certified programs‚ online courses‚ and instructional guides provide comprehensive training for first aid step 3‚ ensuring individuals master practical techniques and best practices for emergency situations․
6․1 Recommended Training Programs for First Aid
Reputable organizations like the American Red Cross and St․ John Ambulance offer structured training programs for first aid step 3‚ focusing on hands-on practice and real-world scenarios; These programs cover essential skills such as CPR‚ wound management‚ and injury assessment‚ ensuring participants are well-prepared for emergencies․ Many courses include certifications‚ validating proficiency in advanced first aid techniques․ Online platforms like Coursera and Udemy also provide accessible training options‚ allowing individuals to learn at their own pace․ These programs emphasize practical application‚ enabling learners to confidently administer care during critical situations․ Regular updates ensure training aligns with the latest medical guidelines‚ fostering a culture of preparedness and competence․
6․2 Online Resources for Learning First Aid Techniques
Various online platforms provide accessible resources for mastering first aid techniques in step 3․ Websites like the American Red Cross and Mayoclinic․org offer detailed guides‚ videos‚ and interactive modules․ YouTube channels such as St․ John Ambulance and First Aid for Life share practical demonstrations․ Additionally‚ free online courses on Coursera and edX cover advanced topics‚ while downloadable PDFs from reputable sources like the British Red Cross offer step-by-step instructions․ These resources allow learners to study at their own pace‚ reinforcing skills like wound care‚ splinting‚ and CPR․ They are invaluable for both beginners and experienced individuals seeking to refresh their knowledge․
6․3 The Role of Certifications in First Aid
Certifications in first aid play a crucial role in ensuring individuals are properly trained and equipped to handle emergencies․ They validate the holder’s ability to perform critical skills‚ such as CPR‚ wound management‚ and trauma care․ Certifications like CPR/AED‚ Basic Life Support (BLS)‚ and Wilderness First Aid are recognized globally‚ enhancing credibility and trust in emergency situations․ Many certifications require hands-on training‚ written exams‚ and periodic renewal‚ ensuring up-to-date knowledge; These credentials are essential for professionals like healthcare workers‚ teachers‚ and workplace first responders‚ as they demonstrate competence and readiness to provide care during the critical third step of first aid․
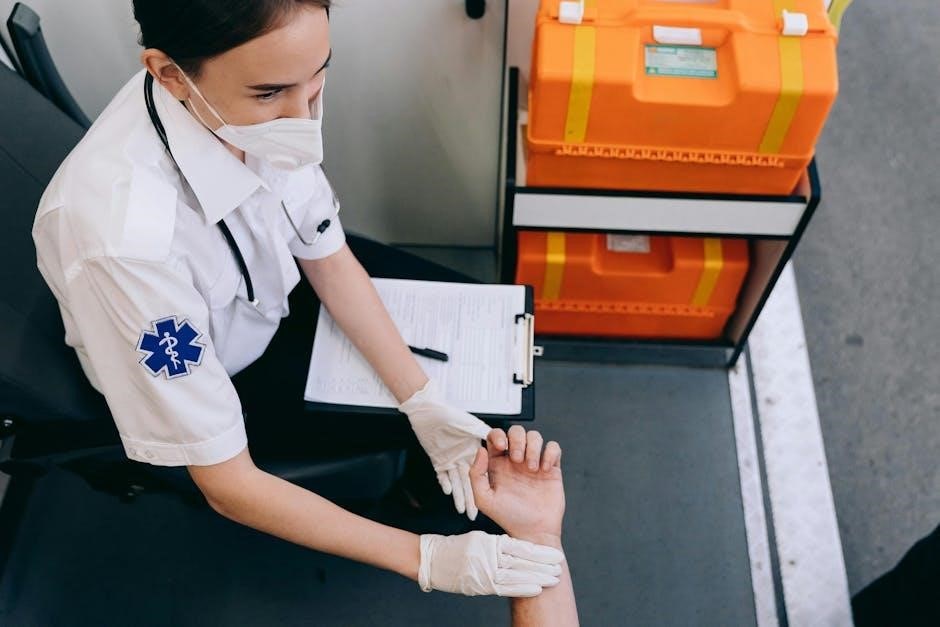
Common Scenarios Requiring the Third Step
Severe injuries‚ burns‚ electrocution‚ or cardiac arrest often demand the third step‚ ensuring timely care to stabilize victims until professional help arrives‚ preventing further complications or fatalities․
7․1 Electrical Shock and Internal Bleeding Incidents
In cases of electrical shock‚ immediately disconnect the power source if safe to do so․ Check the victim’s responsiveness and begin CPR if necessary․ For internal bleeding‚ look for signs like bruising‚ swelling‚ or abdominal pain․ Control external bleeding with direct pressure and elevate the injured area․ Keep the victim calm and comfortable to prevent worsening of the condition․ Monitor vital signs and avoid moving the victim excessively․ These situations require prompt intervention to stabilize the victim until professional medical help arrives‚ as delays can lead to severe complications or fatalities․ Proper care ensures the best chance of recovery and survival․
7․2 Burn Injuries and Splinting Techniques
For burn injuries‚ immediately cool the affected area with cool water for 10-15 minutes․ Remove any clothing or jewelry near the burn without causing further damage․ Cover the burn with a sterile‚ non-stick dressing to prevent infection․ Do not apply ice or butter‚ as this can worsen the injury․ For splinting‚ immobilize fractured limbs to prevent further damage․ Use rigid materials like splints or boards‚ and secure with bandages; Avoid moving the victim excessively and seek professional help promptly․ Proper splinting reduces pain and prevents complications‚ while burn care minimizes scarring and infection risks‚ ensuring optimal recovery outcomes for the victim․
7․3 Shock‚ Poisoning‚ and Seizures
For shock‚ lay the victim on their back‚ elevate legs 12 inches‚ and cover with a blanket to maintain warmth․ Do not give anything to eat or drink․ For poisoning‚ contact a poison control center immediately and follow their instructions․ Never induce vomiting unless advised․ In case of seizures‚ clear the area of sharp objects‚ turn the victim onto their side‚ and do not restrain them․ After the seizure‚ provide reassurance and monitor until recovery․ Seek immediate medical help if the seizure lasts longer than five minutes‚ recurs‚ or is accompanied by injury․ Prompt action is crucial to prevent complications․

The Role of the Community in First Aid
Empowering communities to learn first aid fosters a culture of preparedness‚ ensuring timely and effective response during emergencies․ Collective responsibility enhances safety and saves lives․
8․1 Community Training Programs for Emergency Response
Community training programs are essential for equipping individuals with first aid skills‚ enabling them to respond effectively in emergencies․ These programs‚ often organized by local organizations‚ hospitals‚ or schools‚ provide hands-on workshops and theoretical knowledge․ By teaching techniques like CPR‚ wound care‚ and choking relief‚ participants gain confidence to act decisively․ Such initiatives foster a proactive community‚ reducing response times and improving outcomes․ Regular training updates ensure skills stay current‚ making communities better prepared for various emergencies․ These programs not only save lives but also strengthen collective responsibility for public health and safety․

8․2 Public Awareness Campaigns for First Aid
Public awareness campaigns play a vital role in promoting first aid knowledge and encouraging community participation in emergency response․ These campaigns often utilize social media‚ workshops‚ and educational materials to disseminate information․ By highlighting the importance of immediate action‚ they empower individuals to take charge in critical situations․ Schools and workplaces frequently incorporate these campaigns to ensure widespread reach․ The goal is to reduce hesitation and increase the willingness of bystanders to provide care․ Effective campaigns also address common misconceptions and emphasize the simplicity of life-saving techniques‚ fostering a more prepared and proactive community․
8․3 Building a Culture of Preparedness
Building a culture of preparedness involves fostering a community where first aid is seen as a shared responsibility․ This requires ongoing education‚ regular training sessions‚ and the integration of first aid practices into daily life․ Encouraging individuals to stay informed about potential risks and how to respond can significantly enhance collective readiness․ Communities that prioritize preparedness often see higher rates of successful first aid interventions․ By promoting a proactive mindset‚ societies can reduce the impact of emergencies and create a safer environment for everyone․ Preparedness becomes a collective effort‚ empowering individuals to act confidently when needed․

Legal and Ethical Considerations
Understanding legal and ethical considerations in first aid step 3 is crucial․ It involves knowing Good Samaritan laws‚ ethical duties‚ and liability protections to ensure responsible care․
9․1 Good Samaritan Laws and Their Implications
Good Samaritan laws protect individuals providing first aid in emergencies from legal liability‚ as long as care is given in good faith․ These laws vary by location but generally shield first aid providers from lawsuits unless gross negligence occurs․ They encourage bystanders to assist without fear of legal consequences‚ promoting timely help․ Understanding these laws is essential for first aid providers to act confidently․ They typically apply to unpaid‚ voluntary assistance‚ such as administering CPR or controlling bleeding․ These protections do not require special training‚ making them accessible to everyone․ Knowing these laws ensures providers focus on saving lives rather than legal risks․
9․2 Ethical Dilemmas in Providing First Aid
Providing first aid often involves navigating complex ethical dilemmas‚ such as balancing the duty to help against personal risk․ Decisions may involve allocating limited resources and respecting cultural or religious beliefs that might influence care․ Privacy concerns and consent issues with unconscious patients or minors are also significant․ First responders must weigh the benefits and potential harms of interventions‚ especially when lacking full medical knowledge․ Determining when to cease life-saving efforts and addressing potential biases that might affect care delivery are additional challenges․ Adhering to ethical guidelines ensures compassionate and fair treatment in these critical situations․
9․3 Liability Concerns for First Aid Providers
Liability concerns for first aid providers often stem from the fear of legal consequences if care provided results in unintended harm․ While Good Samaritan laws generally protect individuals who act in good faith during emergencies‚ understanding the boundaries of these protections is crucial․ Providers must ensure they act within the scope of their training and avoid gross negligence․ Maintaining awareness of local laws and following established first aid protocols can help mitigate liability risks․ Additionally‚ documenting the care provided and being mindful of personal limitations are practical steps to safeguard against potential legal issues․ Clear guidelines and proper documentation are essential for minimizing liability risks in first aid situations․
Mastering the third step in first aid is crucial for effective emergency response․ It empowers individuals to provide proper care‚ potentially saving lives․ Stay prepared and informed․
10․1 Summarizing the Importance of the Third Step
The third step in first aid is vital as it bridges the gap between initial assessment and professional medical care․ It ensures that immediate actions are taken to stabilize the victim‚ preventing further harm․ This step emphasizes quick decision-making‚ proper care techniques‚ and effective communication with emergency responders․ By mastering this phase‚ individuals can significantly improve outcomes in critical situations․ Consistent training and knowledge of first aid step 3 empower bystanders to act confidently‚ making a difference in emergencies․ It underscores the importance of preparedness and community involvement in saving lives and reducing recovery time for victims․
10․2 Encouraging Continuous Learning and Preparedness
Continuous learning and preparedness are essential for mastering first aid step 3․ As techniques evolve‚ staying informed ensures effective responses in emergencies․ Regular training sessions and updates from reliable sources‚ like first aid step 3 PDF guides‚ help individuals refine their skills․ Encouraging others to participate in workshops fosters a community of preparedness․ Practicing scenarios and reviewing resources regularly strengthens confidence and competence․ Preparedness also involves maintaining first aid kits and knowing emergency contacts․ By prioritizing ongoing education‚ individuals can provide better care and make a meaningful difference in critical situations․ Continuous learning ensures readiness and improves outcomes in emergencies․